What is the HIPAA Privacy Rule, and Why is it Important?
Data security is crucial in any industry that handles confidential information. However, it is especially important in healthcare because of the nature associated with the data that is being protected. The HIPAA Privacy Rule was established to protect these private medical records. Therefore, having a solid understanding of the HIPAA Privacy Rule summary is a necessity for anyone who regularly handles confidential medical information.
Protected Health Information (PHI) is among some of the most valuable types of data to obtain during a data breach. In fact, it can often be sold for 20 times more than banking information on the Black Market. Above all, it is critical for healthcare entities to preserve the integrity of this data. If not, affected patients could face identity theft, blackmail, or even Medicare fraud.
To keep this highly coveted information safe from unauthorized personnel, HIPAA established a set of rules. Furthermore, the purpose of these rules is to regulate how PHI is used and disclosed in healthcare organizations. Among these includes The Privacy Rule. In the paragraphs below, we will provide a summary of the HIPAA Privacy rule, and discuss why it is important.
A HIPAA Privacy Rule Summary…
The first rule outlined under HIPAA is The Privacy Rule. This legislative subsection was written to identify what kinds of sensitive information is protected under HIPAA. It applies to doctors, insurers, and their contractors- also known as HIPAA covered entities.

The Privacy Rule sets limits on how PHI is used without a patient’s prior authorization. Under The Privacy Rule, a patient has the right to do the following.
- Obtain a copy of their health record.
- Examine their health record.
- Request that corrections be made to their health record.
What does The Privacy Rule NOT Cover?
It is extremely important to understand what The Privacy Rule does cover. However, it is just as important to understand what it does not cover.

- Data handled by an individual or company that is not a CE.
- Employer’s that are not CEs, even if they provide health insurance.
- Data that has been de-identified or made anonymous.
- Most apps and technology companies that handle confidential information, such as health tracking apps, Amazon, Google, etc.
- Data that you generate independently, unless that data is brought to and subsequently handled by a CE.
Why is The Privacy Rule Important?
The Privacy Rule established an important precedent in regards to PHI. In addition, it advocated for a patient’s right to control what rightfully belongs to them. Therefore, it is extremely important for both patients and providers to understand why The Privacy Rule is so important in healthcare.
Without The Privacy Rule, patients would not be aware of their right to medical record ownership. Additionally, there would be no regulations on how that PHI is used by HIPAA covered entities. The Privacy Rule also states that reasonable safeguards need to be put in place by CEs to protect confidential information. These safeguards protect data from unauthorized access.
What is HIPAA?
Did you know that 27% of people are unaware that their Electronic Medical Record (EMR) legally belongs to them? In addition, 41% of American people have never even seen their PHI.
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPPA) gives patients positive control of what is legally theirs. HIPAA laws were established to give patients the opportunity to obtain, keep, and own their health information.

HIPAA laws only apply to Covered Entities (CEs) and Business Associates (BAs. Under HIPAA, CEs and their BAs are required to implement and maintain reasonable, appropriate safeguards to protect confidential medical information.
There are three general rules outlined within the HIPAA laws, The Privacy Rule, The Security Rule, and The Breach Notification Rule. Each of these three guidelines has a unique purpose in regards to properly safeguarding PHI.
What is PHI?
Protected Health Information (PHI) is personal medical information meant to be kept private. In order for this medical information to be considered PHI, it must contain individually identifiable factors. These are characteristics found within the data that make it identifiable to a specific patient.
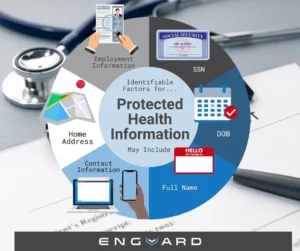
Individually identifiable factors are broad. They can include a patients full name, DOB, SSN, physical address, email, phone number, employment information, or medical history.
Properly safeguarding the integrity of PHI was the catalyst behind the establishment of HIPAA laws. Consequently, healthcare is the most heavily regulated industry in regards to data security because PHI is so valuable. If it is compromised during a data breach, both patients and providers can be faced with detrimental ramifications.
Data Security and The Privacy Rule
As stated under The HIPAA Privacy Rule, sensitive data must be protected. In addition, it regulates the use and disclosure of PHI. This includes Electronic Protected Health Information (ePHI).
ePHI is any form of PHI stored in an electronic capacity. Data security for healthcare providers maintains technical, administrative, and physical safeguards as outlined under HIPAA.

In short, Patient records created, received, or transmitted by healthcare entitles need to be HIPAA compliant. A strong data security strategy can include encrypting data and other access controls.
At Enterprise Guardian, data masking is our top priority. Furthermore, we implement technical safeguards and other information security tactics to protect health data. We will also sign a Business Associate Agreement (BAA) with CEs to ensure that both parties maintain HIPAA compliance.
Is your data secure? Let us take that responsibility off of your hands. Contact our office today to learn more about how our specially curated lines of service can benefit you!

